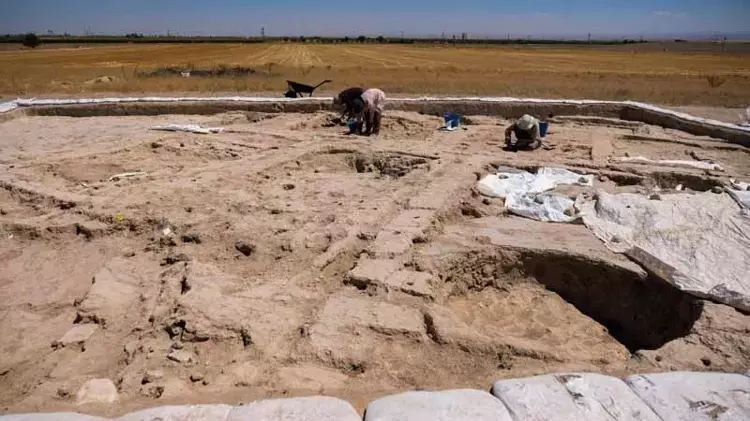

Canhasan 3 Mound may be one of the settlements that prepared the Çatalhöyük culture
Canhasan 3 Mound Excavation Head Assoc. Prof. Dr. Adnan Baysal said, “Canhasan 3 without pottery is a settlement dated 750 years before Çatalhöyük. The paints we encountered on the walls and floor of Canhasan 3 show us that this may be one of the settlements that prepared the Çatalhöyük culture.”
Canhasan 3 Mound is located in the province of Karaman in southern Central Anatolia.
The Canhasan Mounds (I, II and III) were unearthed in the early 1950s as a result of surface surveys conducted under the direction of Dr. David French.
In 2022, excavations resumed under the presidency of Assoc. Prof. Dr. Adnan Baysal, a faculty member at Ankara University, Faculty of Language, History and Geography.
Excavations revealed that Canhasan 1 has Chalcolithic and Neolithic levels and Canhasan 3 belongs to the pottery-free culture.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Baysal said, “Although Canhasan looks like a normal ordinary mound with its typical characteristic air, one of the places that actually makes Canhasan Canhasan is the paleoecology of the Konya Plain. When we look to the east of Karadağ or when we look at the Konya Plain in general, we know that it was completely covered with water 14 thousand years ago.
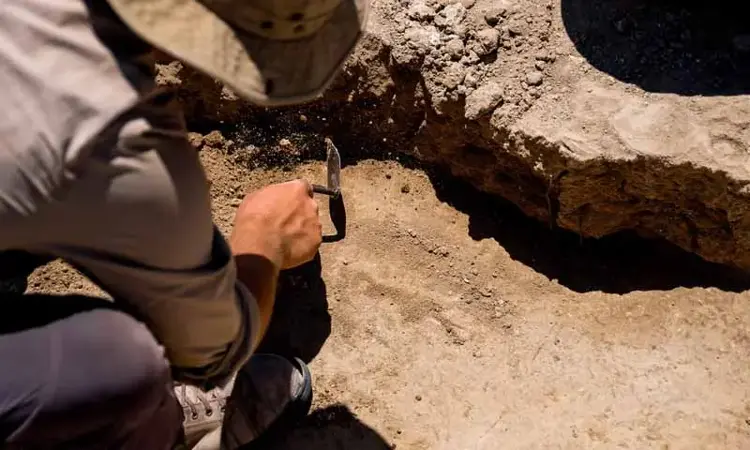

We know this from paleoecological studies, but as a result of these studies, we see that water levels are constantly rising and falling. We see that the waters recede more quickly in this region, and in the examinations we have made, we see that it seems to have been built on the coastal sands. There is a settlement starting with Canhasan 3. Then there is the neolithic settlement, which is also under the chalcolithic settlement.”

Findings show that Canhasan 3 was founded 750 years before Çatalhöyük
While in Anatolia there is generally a mounding system built on top of each other, Canhasan has a horizontal mounding system.
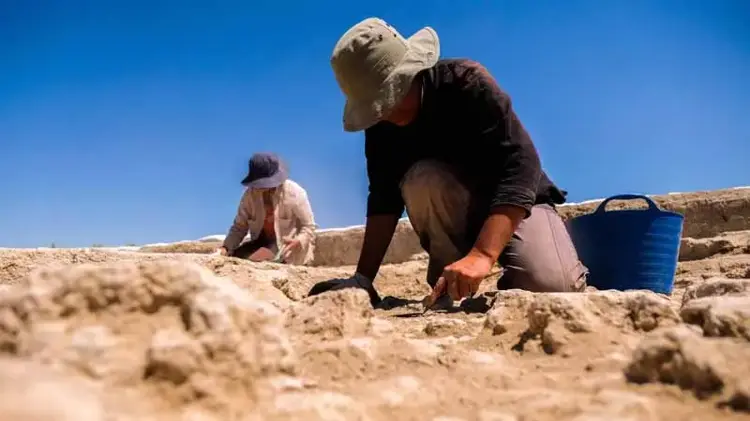

Baysal said that the quadrangular-planned houses unearthed during the studies, the use of space within them, the location of the hearths within this use of space, the places used for storing food in the houses, and the arrangements in these places resemble Çatalhöyük, “but let’s say that Canhasan 3 without pottery is a place dated 750 years earlier. We can say that the paint on the walls and floors of Canhasan 3 is perhaps one of the settlements that prepared the Çatalhöyük culture.”
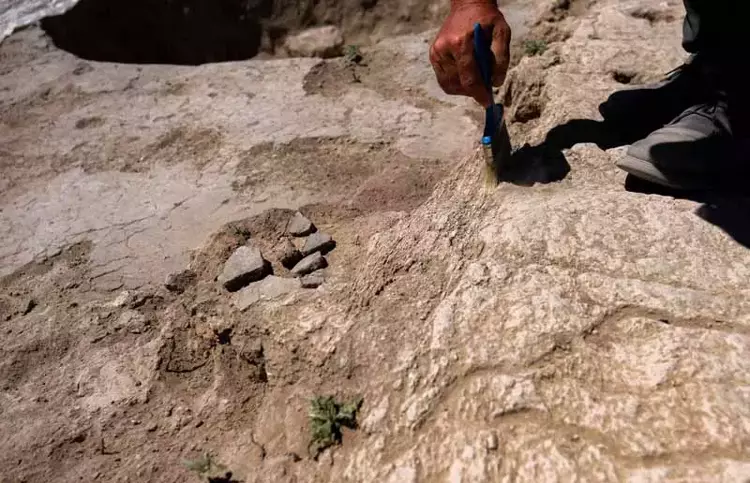

Noting that the houses found during the excavations were painted, Baysal said:
“There are paintings inside the houses. They use manganese oxides to obtain colors such as red paints, types of paints that we can define as iron oxide, and orange colors. The closest place they can go to obtain these is actually the Taurus Mountains. They get this material from there. These people don’t just live in one place. It shows that they have the knowledge and technology to get which materials from where. Of course, they color their world with these colors.
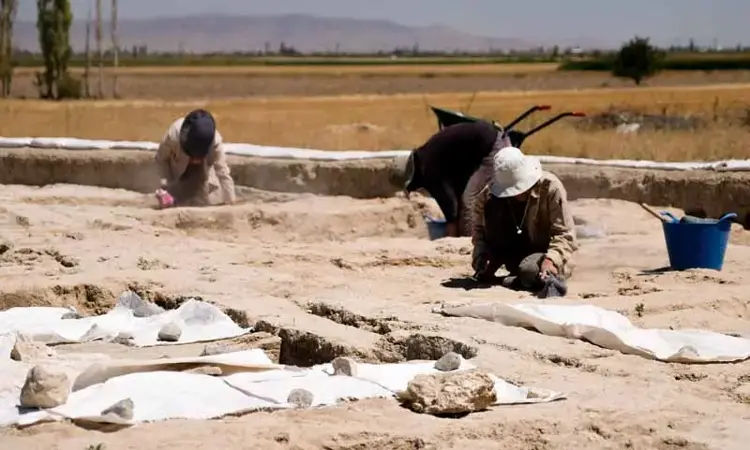

There is a lake between Canhasan 3 and Karadağ. It is such a green environment where reeds grow. Think of a house with white clay floors or red painted houses. They take the white mudbricks from the lake floor, it is an extremely beautiful shining environment. They build a colorful world for themselves, with greenery on one side, red on the inside and black on the floor. I don’t want to romanticize this, but the fact that they live in a very suitable environment probably means that they are aware that they have chosen the right place.”
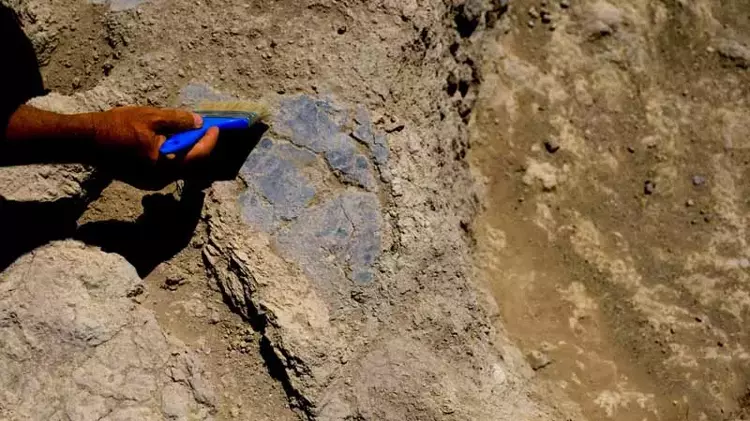

They insulated the walls of their house with lime.
Explaining that they insulated their houses in the region where there are rivers and lakes with lime to protect them from moisture, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Baysal said, “They use plaster hardness or even harder material on the floors of their houses. To say this in line with our current impressions, we need to talk about a floor made by burning lime, and these are really 1.5 centimeter thick floors and painted black. In order to use lime in this way, you had to burn it at that time. I’m talking about a system we call pyro technology, burning lime. They prepared this and spread it on the soles and used it after hardening. So this is a separate technology and we can say that it was one of the first places in Anatolia to be used at that time. They are probably close to the lake, the water level is very high. We think that it may be to minimize the humidity that may come from below or from left and right.”
Cover Photo: DHA
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply