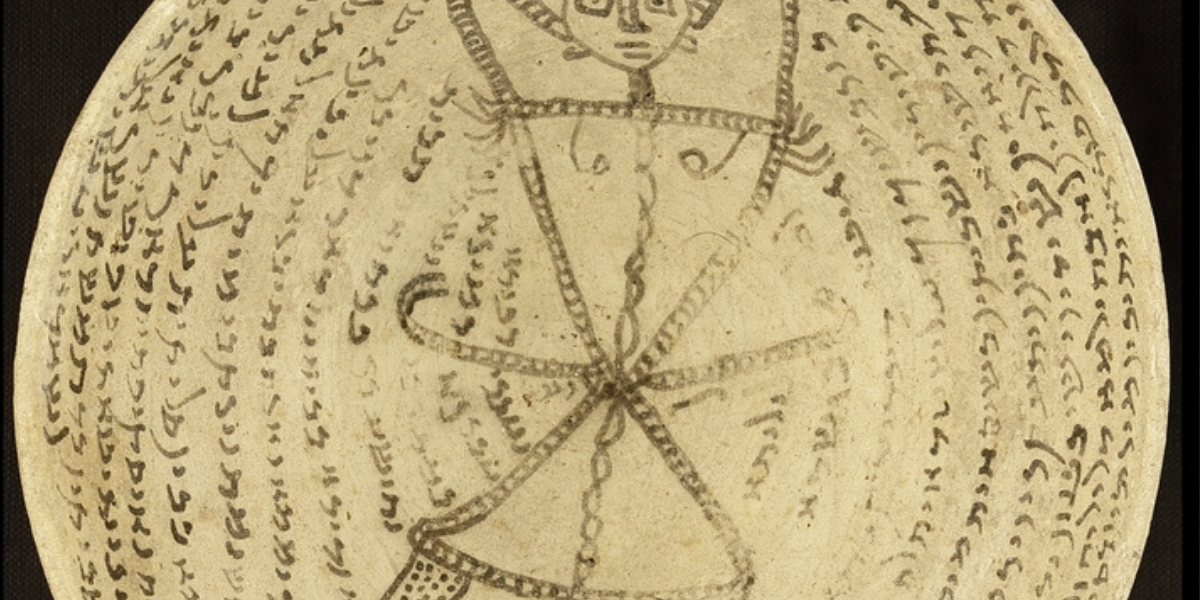
Interesting method of identifying sorcerers in Babylon
Magic is defined as having an effect on people, objects and events through rituals organized by using energy taken from supernatural beings and a number of materials.
People have benefited through magic. Those who cast spells aimed to harm their enemies through magic, to disrupt the peaceful home lives of people they could not attract, and even to ensure their death.
Magic is not only seen as a personal act. There is evidence that magic was used in ancient kingdoms.
Kings resorted to sorcerers for the success of their wars, for the enemy king to fall ill and die, for the enemy people and the state to be cursed and destroyed, and for the crops and animals to be damaged.
Magic was not always used for evil. White magic was used to ensure abundant crops, to help animals produce more offspring, to win the love and affection of a woman or a man, to have children and to overcome diseases and epidemics.
Magic and sorcery have always been forbidden and cursed in every period of history. Those who practiced magic were ostracized in the eyes of society and punished with death.
In the Code of Hammurabi, the method of detection of a sorcerer is “being thrown into water”
In Mesopotamian civilizations, witchcraft was a very common and popular practice. Sumer, Babylon, Akkad, all Mesopotamian peoples supported it.
In the laws written by the Babylonian King Hammurabi, an interesting method to determine whether a person is a sorcerer or not is included in the ritual of “being thrown into water”.
In Article 2 of the Code, the method of “being thrown into water” is written as follows.
“If a man alleges sorcery against another man and cannot prove it, the man who is slandered with sorcery shall go into the river (dive into the river). If the river pulls him out (captures him), the slanderer will take his house (property). If the river cleanses him and brings him to salvation, the man who slandered him will be killed. The man whom the river has brought to salvation will take possession of the slanderer’s property.
The practice of being thrown into water was not only used in Mesopotamia to expose sorcerers. It was also used to exonerate a woman accused of adultery. If she could get out of the river, she was not guilty of adultery, but if she drowned, she was considered to have committed adultery.
The exoneration or death that resulted from being thrown into the water was believed to be a manifestation of the will of the gods.
Cover Photo: The National Library of Israel, Jerusalem, Israel
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply