
Assyriologist makes new interpretations of ancient symbols in a 2,700-year-old temple
Assyriologist Dr. Martin Worthington has made new interpretations of ancient symbols found in a 2,700-year-old temple in the ancient city of Dur-Šarrukin, home to King Sargón II, ruler of Assyria from 721-704 BC.
Dur-Šarrukin is located in Khorsabad, in present-day Iraq. Dur-Šarrukin means “fortress of Sargon”.
Sargon II, who built Dur-Sharrukin (Khorsabad), was given the title “Sharru-kinu” (True King) upon his accession to the throne, although his real name is unknown.
After rising to a high rank in the Assyrian army, he ascended to the throne upon the death of Tiglath-Pileser III in 722 BC.
During his reign, he expanded the Assyrian Empire to Babylon in the west and Urartu in the east. He conquered the Kingdom of Israel and exiled the Israelites.
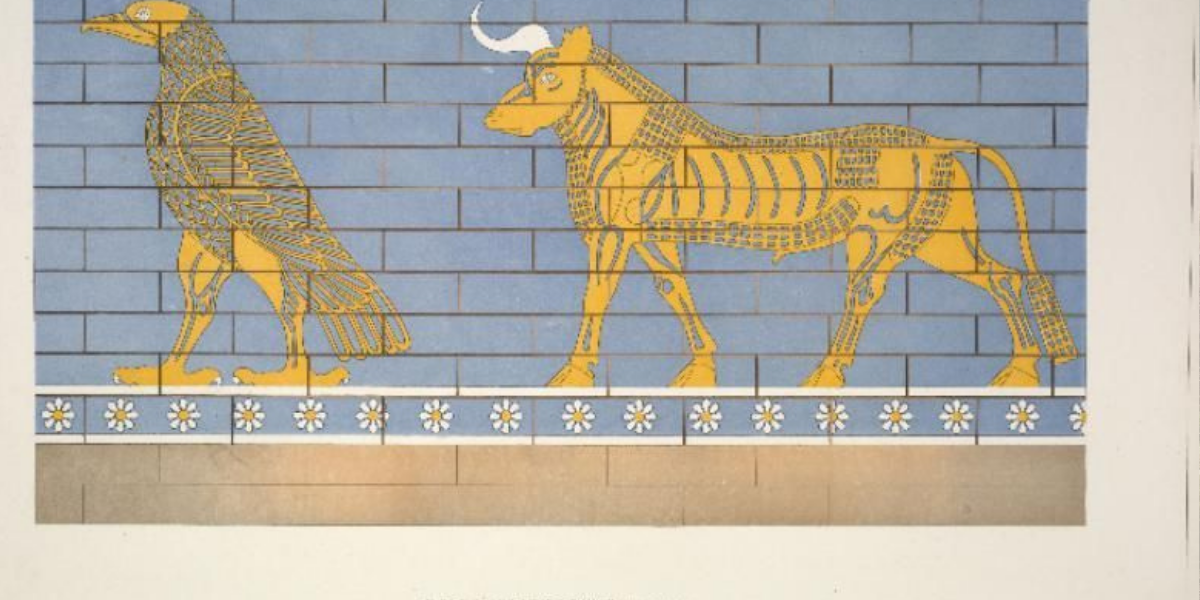
The symbols of the lion, eagle, bull, fig tree and plow were reinterpreted in the 2700-year-old temple in the city of Dur-Sharrukin’i (Khorsabad), which was majestically designed to show the power and glory of Assyria.
These symbols and others like them were documented by French excavators who visited the site at the end of the 19th century.
Since their discovery, many researchers have tried to interpret their meaning. Some believe they are like Egyptian hieroglyphs, a kind of expression of imperial power, and could even spell the name of the king. But how these connections can be made remains a mystery.
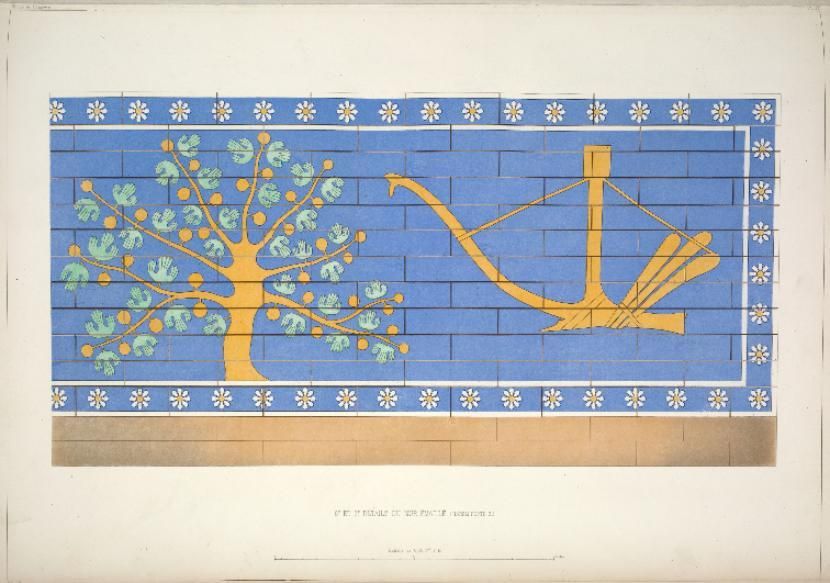
An Assyriologist named Dr. Martin Worthington of Trinity College in Dublin has presented a convincing analysis of these symbols that has the potential to completely change our perception of ancient Mesopotamian iconography.
In a recent article in the Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, Dr. Worthington put forward a groundbreaking hypothesis: A sequence of five symbols could spell Sargon’s name (šargīnu) and also represent specific constellations.
“The study of ancient languages and cultures is full of puzzles of all shapes and sizes, but it is not often that one encounters mysterious symbols on a temple wall in the Ancient Near East,” Dr. Worthington said in a statement.

Moreover, according to Dr. Worthington, each of the five symbols can also be understood as a constellation. Thus, the lion represents Leo and the eagle Aquila (our own constellations were largely inherited from Mesopotamia, through the Greeks, so many are the same). The fig tree represents the elusive ‘Jaw’ constellation (which we don’t have today) on the basis that the word iṣu ‘tree’ sounds similar to isu’jaw.
“The effect of the five symbols was to place Sargon’s name forever in heaven – a clever way of making the king’s name immortal. And of course, the idea of extravagant individuals inscribing their names on buildings is not unique to ancient Assyria…”
Although Dr. Worthington admits that his theory cannot be proven beyond a reasonable doubt, the fact that it holds true for both the longer three-symbol sequence and the five-symbol sequence suggests it is more than just a coincidence.
Cover Photo: Late 19th-century drawings of the eagle and bull symbols published by French excavator Victor Place. From New York Public Library.
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply